The map operator in Combine is a powerful tool that lets you transform data flowing through a publisher. In reactive programming, transforming data is a common task, and map makes it easy to adapt publisher values to suit your needs. With map, you can take any value emitted by a publisher, apply a transformation function, and pass the transformed value down the pipeline to subscribers.
What is the map Operator?
In Combine, the map operator is used to transform the output of a publisher by applying a function to each value it emits. The function you provide to map takes the current value from the publisher and returns a new value based on the transformation. This is especially useful in SwiftUI because you often need to adapt data for display or further processing.
For example, you might use map to:
- Convert numbers to formatted strings.
- Transform model data into user-readable descriptions.
- Adjust boolean values to text labels or colors.
In this article, we’ll create a SwiftUI view that uses map to transform a number into a formatted string for display.
Example SwiftUI View with map
Below is a SwiftUI view that uses a PassthroughSubject to emit random numbers and the map operator to format each number as a string with specific formatting.
import SwiftUI
import Combine
struct MapOperatorExampleView: View {
// State variable to display the formatted number
@State private var formattedNumber: String = "Press the button to get a random number"
// PassthroughSubject to publish random numbers
private let numberPublisher = PassthroughSubject<Int, Never>()
// AnyCancellable to store the subscription
@State private var cancellable: AnyCancellable?
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
Text("Map Operator Example")
.font(.headline)
.padding()
Text(formattedNumber) // Display the formatted number
.font(.title)
.padding()
Button("Generate Random Number") {
// Send a random number through the publisher
let randomNum = Int.random(in: 1...100)
numberPublisher.send(randomNum)
}
.padding()
.background(Color.green)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(8)
}
.onAppear {
// Use the map operator to transform the random number into a formatted string
cancellable = numberPublisher
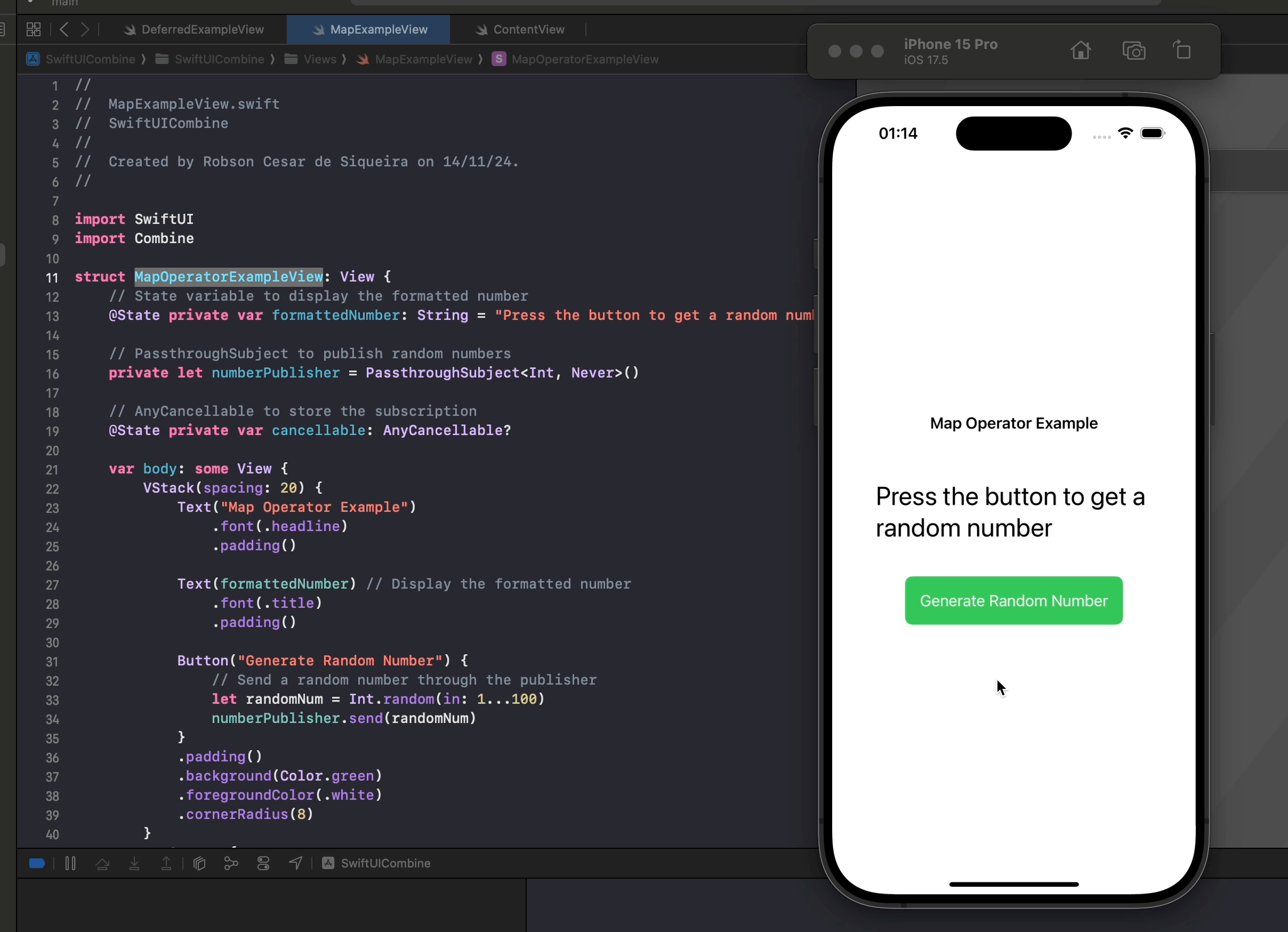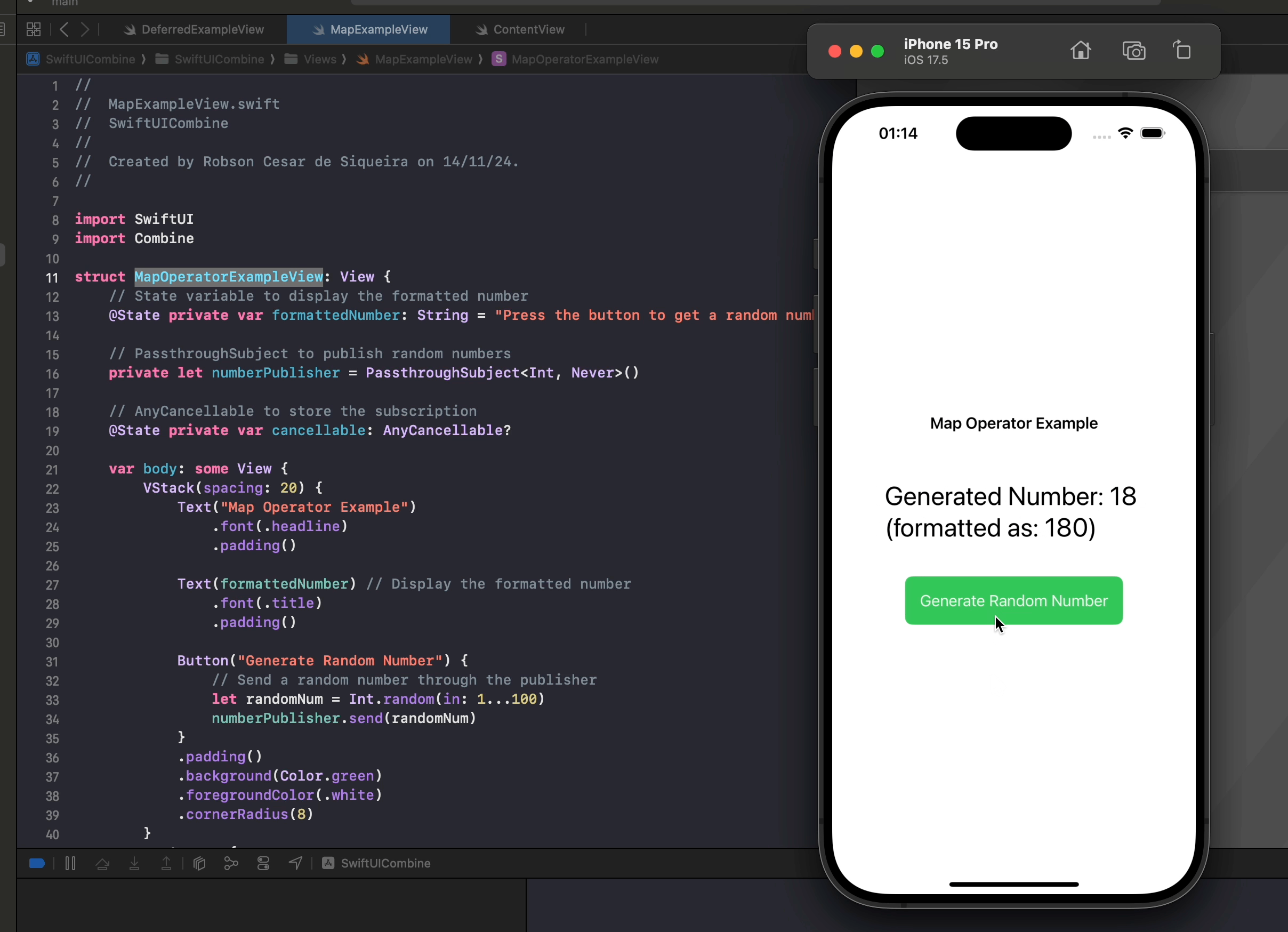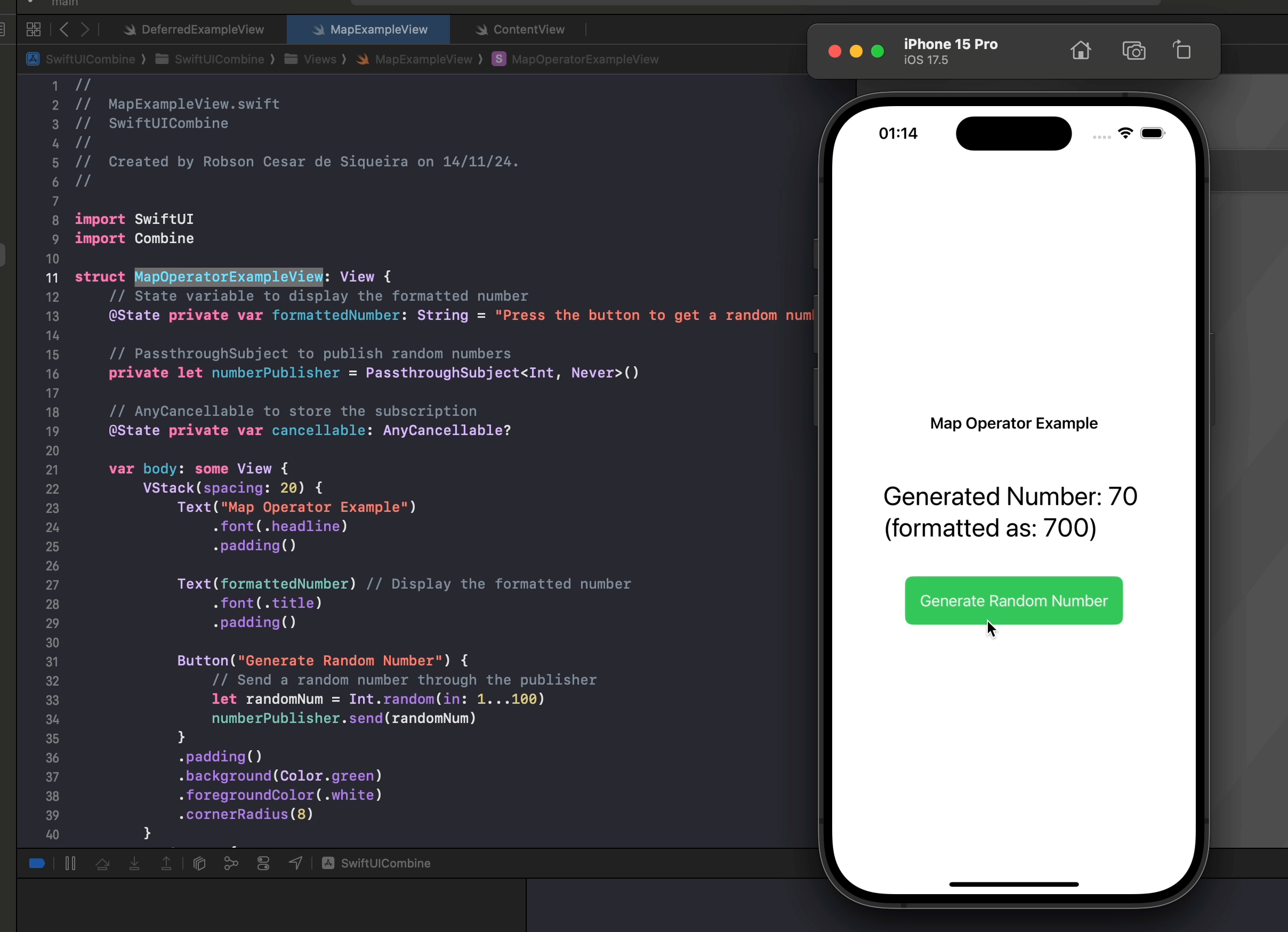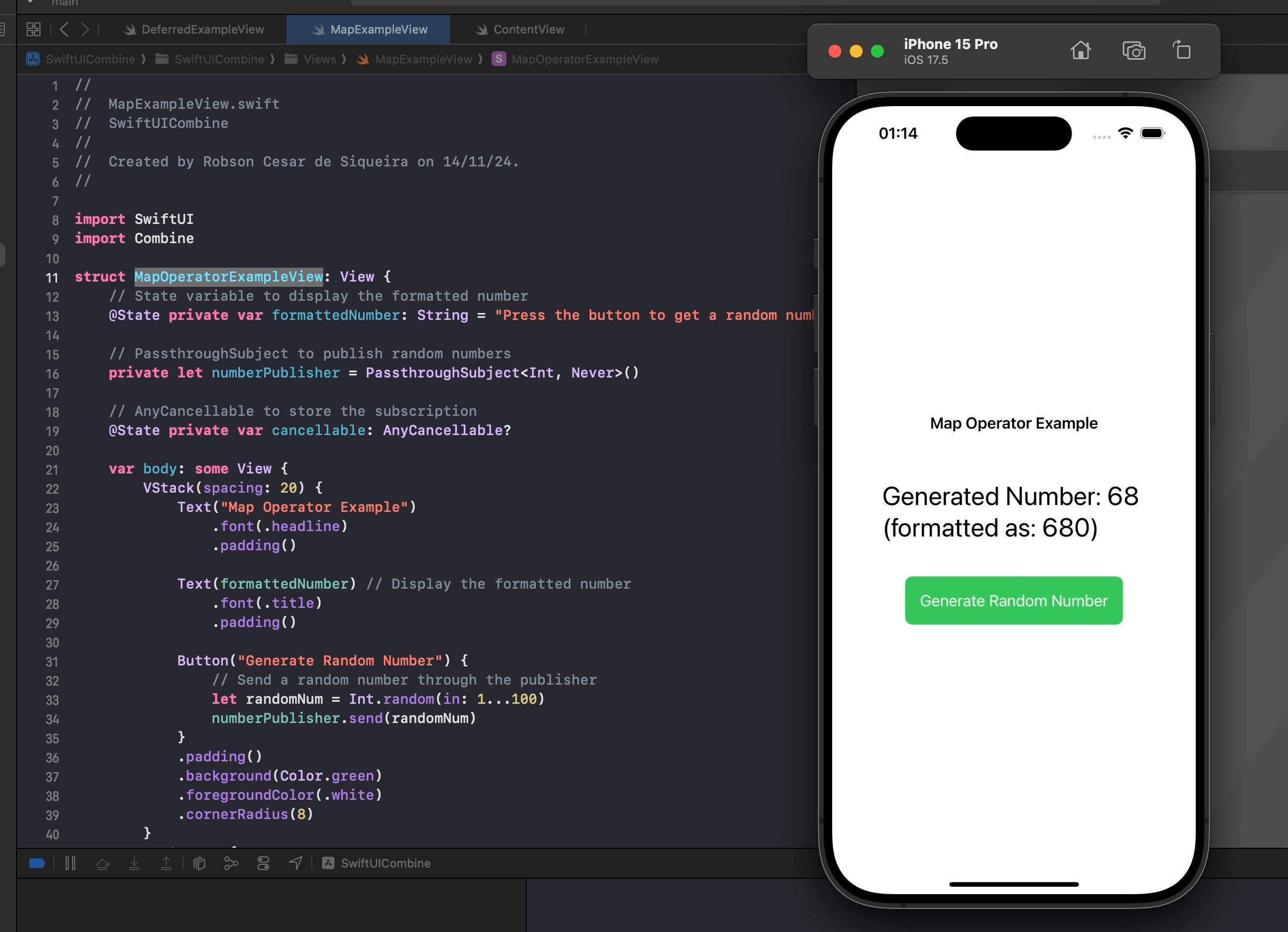
.map { number in
"Generated Number: \(number) (formatted as: \(number * 10))"
}
.sink { formattedValue in
formattedNumber = formattedValue
}
}
.onDisappear {
// Cancel the subscription when the view disappears
cancellable?.cancel()
}
}
}
struct MapOperatorExampleView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
MapOperatorExampleView()
}
}
Explanation of the Code
- State Variable:
@State private var formattedNumber: Holds the formatted string that’s displayed in the view. This value updates whenever a new number is emitted by thenumberPublisher.
- PassthroughSubject:
private let numberPublisher = PassthroughSubject<Int, Never>(): This publisher emits integer values and has aNeverfailure type, meaning it does not produce errors.
- Button to Emit a Random Number:
- The Generate Random Number button generates a random number between 1 and 100 and sends it through
numberPublisher. This triggers themapoperator to transform the number.
- The Generate Random Number button generates a random number between 1 and 100 and sends it through
- The
mapOperator:- Inside
.onAppear, we set up themapoperator onnumberPublisherto transform each emitted number into a formatted string. The transformation function takesnumberas input and returns a string with some additional formatting, including multiplying the number by 10. - The transformed value is then handled by
.sink, which updatesformattedNumber, causing SwiftUI to refresh the view with the new string.
- Inside
- Cleaning Up the Subscription:
- The
.onDisappearmodifier cancels the subscription when the view disappears, preventing memory leaks and stopping updates when the view is no longer on screen.
- The
How map Helps in SwiftUI
In this example, map allows us to dynamically transform numbers into displayable strings with custom formatting. Each time a new random number is sent, the map operator applies the transformation, creating a unique string. SwiftUI then automatically observes the updated string and displays it in the view.
Summary
The map operator in Combine is one of the most flexible and frequently used tools, allowing you to transform data as it flows through publishers. This makes it easy to adapt raw data to user-friendly formats, create complex UI representations, and even perform lightweight computations. In SwiftUI, map works perfectly for transforming data in a reactive, observable way, which helps you build responsive and interactive user interfaces.